
Typically, patients report at least 3 episodes of non-bloody diarrhea per day. If you have trouble remembering the words, then you may substitute Happy Birthday To You.Ĭlinical manifestation can range from asymptomatic to fulminant colitis and sepsis. The hands must be lathered with soap, and the soap must stay in contact with the hands for as long as it takes to twice slowly sing Row RowRow Your Boat. Simply slapping a little bit of soap on the hands and then wiping, will do nothing to eradicate C. The quality of the handwashing is important. diff spores have an inherent resistance to alcohol and alcohol-based hand sanitizers, hand washing with soap and water by medical staff and family members is important. If inanimate surfaces are not properly cleaned, reinfection becomes a real possibility and problem. The spores may survive for weeks or months on inanimate objects and may account for widespread outbreaks within hospitals and nursing facilities. Infection can be spread through the fecal-oral route when spores are ingested. Particularly at risk are individuals over age 60, those who have had prolonged antibiotic treatment, and patients who have undergone irradiation or have obstructive pulmonary disease, malignancy, mechanical bowel preparation prior to colonic surgery, enteral feeding, ICU care and those who are immunosuppressed. diff infection, the most frequent offending antibiotics include cephalosporins, penicillins, and clindamycin. While nearly all antibiotics have been associated with causing a C. diff infection is invariably related to prior antibiotic use which suppresses the normal colonic flora, thereby allowing selective growth of C.

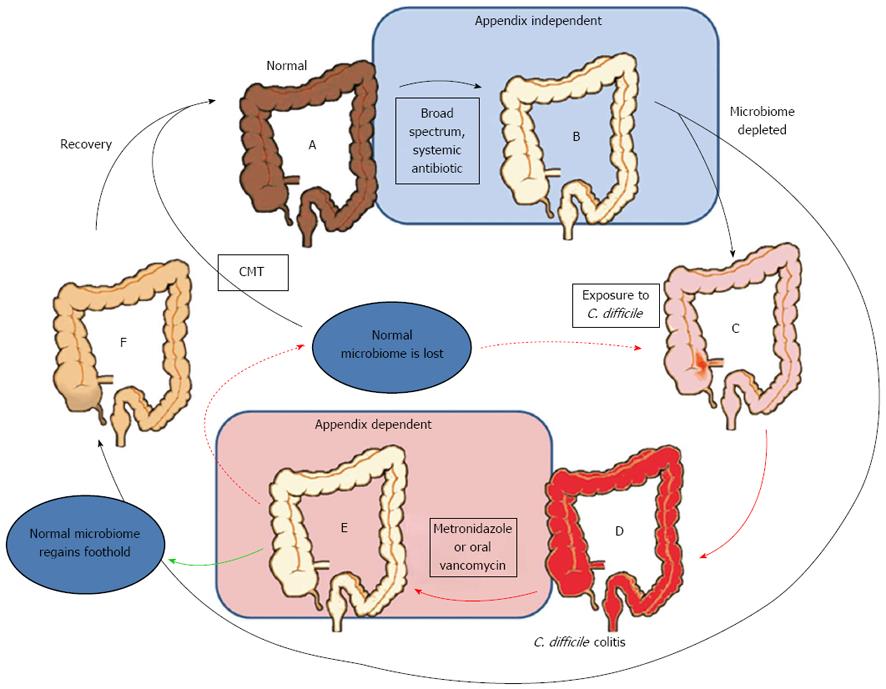
Clostridium difficile is a normal minor inhabitant of the intestinal microbiome. A macrophage response leads to release of tumor necrosis factor and Interleukins 1 and 6, which are responsible for the systemic septic reaction. This process leads to a secretory diarrhea, with an inflammatory reaction which can culminate in cell death. Toxin A causes increased colonic permeability and fluid secretion, while toxin B causes colonic inflammation. diff causes colitis and subsequent diarrhea by release of exotoxins referred to as Toxin A (enterotoxin) and Toxin B (cytotoxin).Δ The Pathology of the Inflammatory Response.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
